PHYSIK → Klasse 9 & 10 → Project Car
Wozu das Project Car?
Aufbau
Das Auto besteht aus sechs Hauptkomponenten: Microcontroler (ESP32 DevModul), Motortreiber (L289N), Motoren (DC 12V Getriebemotoren), Stromversorgung und Gamepad (Steuerung)
 In diesem Aufbau wird dem Microcontroler über Bluetooth von einem Gamepad Bewegungsdaten gesendet. Diese werden dort in passende Signale umgewandelt, welche dann an den Motortreiber weitergesendet werden. Der Motortreiber steuert die Gleichspannungsmotorn an und versorgt diese mit der passenden Spannung. Die Spannungsversorung ist direkt am Motortreiber angeschlossen, welcher dadurch ebenfalls den Microcobntroller mit Strom versorgen kann.
In diesem Aufbau wird dem Microcontroler über Bluetooth von einem Gamepad Bewegungsdaten gesendet. Diese werden dort in passende Signale umgewandelt, welche dann an den Motortreiber weitergesendet werden. Der Motortreiber steuert die Gleichspannungsmotorn an und versorgt diese mit der passenden Spannung. Die Spannungsversorung ist direkt am Motortreiber angeschlossen, welcher dadurch ebenfalls den Microcobntroller mit Strom versorgen kann.
Das Herzstück des Modellautos bidlet der Microcontroller. Alle grundlegenden Infos zu dem hier verwendeten Modell können unter diesem Link nachgeschlagen werden. Das PIN Layout des ESP32 DevKit V4 wird in folgender Abbildung dargestellt:
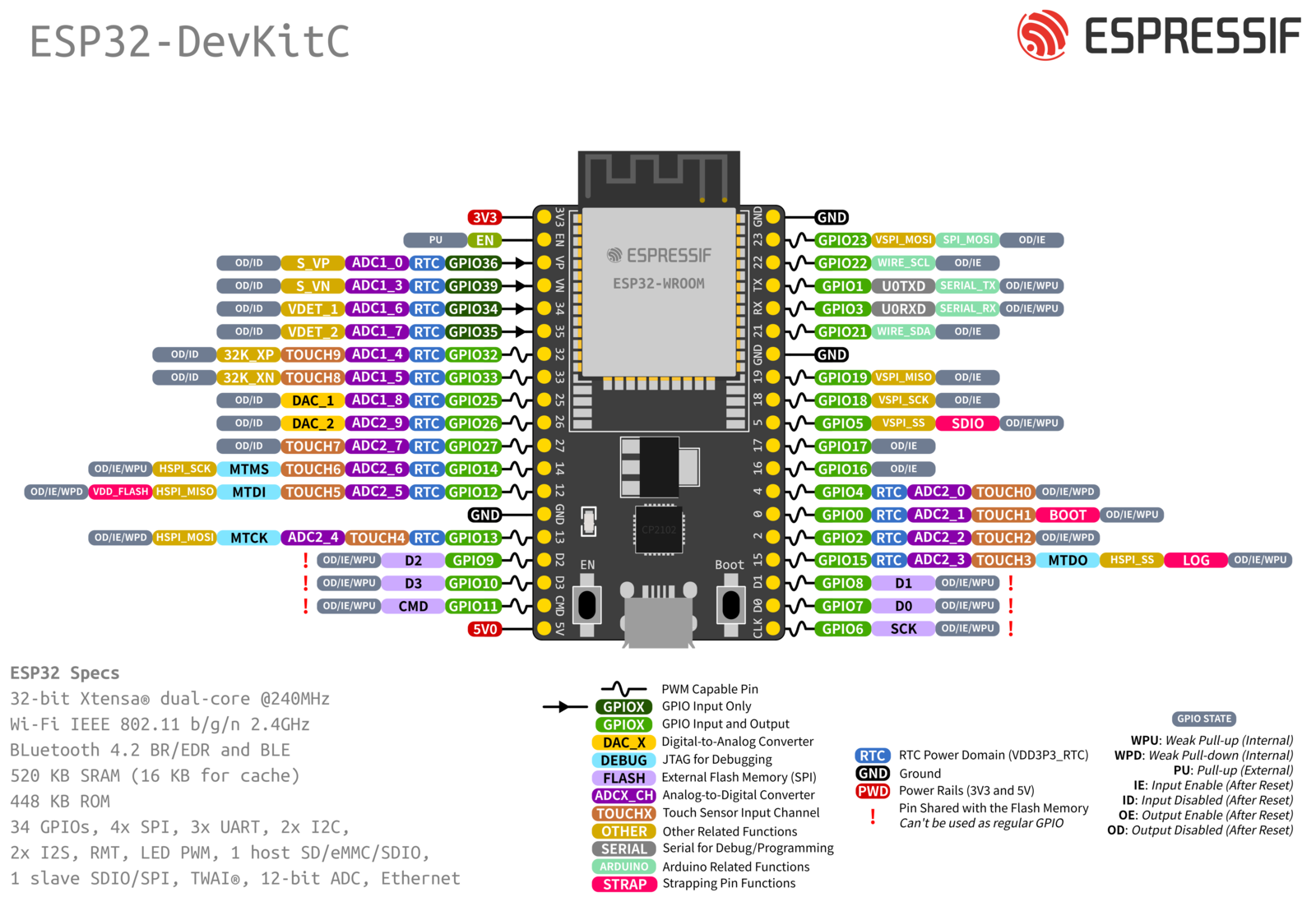

Anleitung
Die Komponenten werden über folgenden Schaltplan zusammengebaut:

Code
Für die Steuerung des Autos mithilfe des Bluetoothcontrollers benötigen wir ausschließlich folgende library:
//set Board to ESP32 Dev Modul and select port
//needed libraries
#include <Bluepad32.h> //bluetooth connection with gamepad and read values from gamepad
In unserem Aufbau sind die Pins wie folgt belegt:
// PIN CONNECTIONS between motordriver and ESP32
int ENApin = 14; //P14
int IN1pin = 27; //P27
int IN2pin = 26; //P26
int IN3pin = 25; //P25
int IN4pin = 33; //P33
int ENBpin = 32; //P32
Zur Verbindung des Controllers via Bluetooth mit dem ESP benötigen wir folgenden Code:
ControllerPtr myControllers[BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS];
// This callback gets called any time a new gamepad is connected.
// Up to 4 gamepads can be connected at the same time.
void onConnectedController(ControllerPtr ctl) {
bool foundEmptySlot = false;
for (int i = 0; i < BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS; i++) {
if (myControllers[i] == nullptr) {
Serial.printf("CALLBACK: Controller is connected, index=%d\n", i);
// Additionally, you can get certain gamepad properties like:
// Model, VID, PID, BTAddr, flags, etc.
ControllerProperties properties = ctl->getProperties();
Serial.printf("Controller model: %s, VID=0x%04x, PID=0x%04x\n", ctl->getModelName().c_str(), properties.vendor_id, properties.product_id);
myControllers[i] = ctl;
foundEmptySlot = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundEmptySlot) {
Serial.println("CALLBACK: Controller connected, but could not found empty slot");
}
}
void onDisconnectedController(ControllerPtr ctl) {
bool foundController = false;
for (int i = 0; i < BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS; i++) {
if (myControllers[i] == ctl) {
Serial.printf("CALLBACK: Controller disconnected from index=%d\n", i);
myControllers[i] = nullptr;
foundController = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundController) {
Serial.println("CALLBACK: Controller disconnected, but not found in myControllers");
}
}
Um die Eingangssignae vom Controller am ESP zu verarbeiten, werden die Signalwerte entsprechende Variablen zugeordnet, welche anschließend in Signale an die Pins, um die gewünschte Bewegungs auszuführen, uminterpretiert werden.
// ========= SEE CONTROLLER VALUES IN SERIAL MONITOR ========= //
void dumpGamepad(ControllerPtr ctl) {
Serial.printf(
"idx=%d, dpad: 0x%02x, buttons: 0x%04x, axis L: %4d, %4d, axis R: %4d, %4d, brake: %4d, throttle: %4d, "
"misc: 0x%02x, gyro x:%6d y:%6d z:%6d, accel x:%6d y:%6d z:%6d\n",
ctl->index(), // Controller Index
ctl->dpad(), // D-pad
ctl->buttons(), // bitmask of pressed buttons
ctl->axisX(), // (-511 - 512) left X Axis
ctl->axisY(), // (-511 - 512) left Y axis
ctl->axisRX(), // (-511 - 512) right X axis
ctl->axisRY(), // (-511 - 512) right Y axis
ctl->brake(), // (0 - 1023): brake button
ctl->throttle(), // (0 - 1023): throttle (AKA gas) button
ctl->miscButtons(), // bitmask of pressed "misc" buttons
ctl->gyroX(), // Gyro X
ctl->gyroY(), // Gyro Y
ctl->gyroZ(), // Gyro Z
ctl->accelX(), // Accelerometer X
ctl->accelY(), // Accelerometer Y
ctl->accelZ() // Accelerometer Z
);
}
// ========= GAME CONTROLLER ACTIONS SECTION ========= //
void processGamepad(ControllerPtr ctl) {
// There are different ways to query whether a button is pressed.
// By query each button individually:
// a(), b(), x(), y(), l1(), etc...
//== PS4 X button = 0x0001 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0001) {
// code for when X button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0001) {
// code for when X button is released
}
//== PS4 Square button = 0x0004 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0004) {
// code for when square button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0004) {
// code for when square button is released
}
//== PS4 Triangle button = 0x0008 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0008) {
// code for when triangle button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0008) {
// code for when triangle button is released
}
//== PS4 Circle button = 0x0002 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0002) {
// code for when circle button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0002) {
// code for when circle button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad UP button = 0x01 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x01) {
// code for when dpad up button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x01) {
// code for when dpad up button is released
}
//==PS4 Dpad DOWN button = 0x02==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x02) {
// code for when dpad down button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x02) {
// code for when dpad down button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad LEFT button = 0x08 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x08) {
// code for when dpad left button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x08) {
// code for when dpad left button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad RIGHT button = 0x04 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x04) {
// code for when dpad right button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x04) {
// code for when dpad right button is released
}
//== PS4 R1 trigger button = 0x0020 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0020) {
// code for when R1 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0020) {
// code for when R1 button is released
}
//== PS4 R2 trigger button = 0x0080 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0080) {
// code for when R2 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0080) {
// code for when R2 button is released
}
//== PS4 L1 trigger button = 0x0010 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0010) {
// code for when L1 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0010) {
// code for when L1 button is released
}
//== PS4 L2 trigger button = 0x0040 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0040) {
// code for when L2 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0040) {
// code for when L2 button is released
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - UP ==//
if (ctl->axisY() <= -100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisY(), -100, -508, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed up
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - DOWN ==//
if (ctl->axisY() >= 100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisY(), 100, 512, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, HIGH);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed down
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - LEFT ==//
if (ctl->axisX() <= -100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisX(), -100, -508, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, 0);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed left
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - RIGHT ==//
if (ctl->axisX() >= 100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisX(), 100, 512, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, 0);
// code for when left joystick is pushed right
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK DEADZONE ==//
if (ctl->axisY() > -100 && ctl->axisY() < 100 && ctl->axisX() > -100 && ctl->axisX() < 100) {
analogWrite(ENApin, 0);
analogWrite(ENBpin, 0);
// code for when left joystick is at idle
}
//== RIGHT JOYSTICK - X AXIS ==//
if (ctl->axisRX()) {
// code for when right joystick moves along x-axis
}
//== RIGHT JOYSTICK - Y AXIS ==//
if (ctl->axisRY()) {
// code for when right joystick moves along y-axis
}
dumpGamepad(ctl);
}
Die Werte ab denen eine Bewegungs ausgeführt wird und wie hoch die Spannung an den Pins sein soll, also wie stark das Auto beschleunig bzw. sich dreht können im Nachhinein angepasst werden.
Damit das ESP die Kommunikation mit dem Controller ausführt, muss folgender Code verwendet werden:
void processControllers() {
for (auto myController : myControllers) {
if (myController && myController->isConnected() && myController->hasData()) {
if (myController->isGamepad()) {
processGamepad(myController);
} else {
Serial.println("Unsupported controller");
}
}
}
}
// Arduino setup function. Runs in CPU 1
void setup() {
pinMode(ENApin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENBpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4pin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.printf("Firmware: %s\n", BP32.firmwareVersion());
const uint8_t* addr = BP32.localBdAddress();
Serial.printf("BD Addr: %2X:%2X:%2X:%2X:%2X:%2X\n", addr[0], addr[1], addr[2], addr[3], addr[4], addr[5]);
// Setup the Bluepad32 callbacks
BP32.setup(&onConnectedController, &onDisconnectedController);
// "forgetBluetoothKeys()" should be called when the user performs
// a "device factory reset", or similar.
// Calling "forgetBluetoothKeys" in setup() just as an example.
// Forgetting Bluetooth keys prevents "paired" gamepads to reconnect.
// But it might also fix some connection / re-connection issues.
BP32.forgetBluetoothKeys();
// Enables mouse / touchpad support for gamepads that support them.
// When enabled, controllers like DualSense and DualShock4 generate two connected devices:
// - First one: the gamepad
// - Second one, which is a "virtual device", is a mouse.
// By default, it is disabled.
BP32.enableVirtualDevice(false);
// Serial port for debugging purposes
}
// Arduino loop function. Runs in CPU 1.
void loop() {
// This call fetches all the controllers' data.
// Call this function in your main loop.
//Serial.println(readDHTTemperature());
//Serial.println(readDHTHumidity());
bool dataUpdated = BP32.update();
if (dataUpdated)
processControllers();
// The main loop must have some kind of "yield to lower priority task" event.
// Otherwise, the watchdog will get triggered.
// If your main loop doesn't have one, just add a simple `vTaskDelay(1)`.
// Detailed info here:
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/66278271/task-watchdog-got-triggered-the-tasks-did-not-reset-the-watchdog-in-time
// vTaskDelay(1);
delay(150);
}
//set Board to ESP32 Dev Modul and select port
//needed libraries
#include <Bluepad32.h> //bluetooth connection with gamepad and read values from gamepad// PIN CONNECTIONS between motordriver and ESP32
int ENApin = 14; //P14
int IN1pin = 27; //P27
int IN2pin = 26; //P26
int IN3pin = 25; //P25
int IN4pin = 33; //P33
int ENBpin = 32; //P32ControllerPtr myControllers[BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS];
// This callback gets called any time a new gamepad is connected.
// Up to 4 gamepads can be connected at the same time.
void onConnectedController(ControllerPtr ctl) {
bool foundEmptySlot = false;
for (int i = 0; i < BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS; i++) {
if (myControllers[i] == nullptr) {
Serial.printf("CALLBACK: Controller is connected, index=%d\n", i);
// Additionally, you can get certain gamepad properties like:
// Model, VID, PID, BTAddr, flags, etc.
ControllerProperties properties = ctl->getProperties();
Serial.printf("Controller model: %s, VID=0x%04x, PID=0x%04x\n", ctl->getModelName().c_str(), properties.vendor_id, properties.product_id);
myControllers[i] = ctl;
foundEmptySlot = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundEmptySlot) {
Serial.println("CALLBACK: Controller connected, but could not found empty slot");
}
}
void onDisconnectedController(ControllerPtr ctl) {
bool foundController = false;
for (int i = 0; i < BP32_MAX_GAMEPADS; i++) {
if (myControllers[i] == ctl) {
Serial.printf("CALLBACK: Controller disconnected from index=%d\n", i);
myControllers[i] = nullptr;
foundController = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundController) {
Serial.println("CALLBACK: Controller disconnected, but not found in myControllers");
}
}// ========= SEE CONTROLLER VALUES IN SERIAL MONITOR ========= //
void dumpGamepad(ControllerPtr ctl) {
Serial.printf(
"idx=%d, dpad: 0x%02x, buttons: 0x%04x, axis L: %4d, %4d, axis R: %4d, %4d, brake: %4d, throttle: %4d, "
"misc: 0x%02x, gyro x:%6d y:%6d z:%6d, accel x:%6d y:%6d z:%6d\n",
ctl->index(), // Controller Index
ctl->dpad(), // D-pad
ctl->buttons(), // bitmask of pressed buttons
ctl->axisX(), // (-511 - 512) left X Axis
ctl->axisY(), // (-511 - 512) left Y axis
ctl->axisRX(), // (-511 - 512) right X axis
ctl->axisRY(), // (-511 - 512) right Y axis
ctl->brake(), // (0 - 1023): brake button
ctl->throttle(), // (0 - 1023): throttle (AKA gas) button
ctl->miscButtons(), // bitmask of pressed "misc" buttons
ctl->gyroX(), // Gyro X
ctl->gyroY(), // Gyro Y
ctl->gyroZ(), // Gyro Z
ctl->accelX(), // Accelerometer X
ctl->accelY(), // Accelerometer Y
ctl->accelZ() // Accelerometer Z
);
}
// ========= GAME CONTROLLER ACTIONS SECTION ========= //
void processGamepad(ControllerPtr ctl) {
// There are different ways to query whether a button is pressed.
// By query each button individually:
// a(), b(), x(), y(), l1(), etc...
//== PS4 X button = 0x0001 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0001) {
// code for when X button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0001) {
// code for when X button is released
}
//== PS4 Square button = 0x0004 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0004) {
// code for when square button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0004) {
// code for when square button is released
}
//== PS4 Triangle button = 0x0008 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0008) {
// code for when triangle button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0008) {
// code for when triangle button is released
}
//== PS4 Circle button = 0x0002 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0002) {
// code for when circle button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0002) {
// code for when circle button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad UP button = 0x01 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x01) {
// code for when dpad up button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x01) {
// code for when dpad up button is released
}
//==PS4 Dpad DOWN button = 0x02==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x02) {
// code for when dpad down button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x02) {
// code for when dpad down button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad LEFT button = 0x08 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x08) {
// code for when dpad left button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x08) {
// code for when dpad left button is released
}
//== PS4 Dpad RIGHT button = 0x04 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x04) {
// code for when dpad right button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x04) {
// code for when dpad right button is released
}
//== PS4 R1 trigger button = 0x0020 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0020) {
// code for when R1 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0020) {
// code for when R1 button is released
}
//== PS4 R2 trigger button = 0x0080 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0080) {
// code for when R2 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0080) {
// code for when R2 button is released
}
//== PS4 L1 trigger button = 0x0010 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0010) {
// code for when L1 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0010) {
// code for when L1 button is released
}
//== PS4 L2 trigger button = 0x0040 ==//
if (ctl->buttons() == 0x0040) {
// code for when L2 button is pushed
}
if (ctl->buttons() != 0x0040) {
// code for when L2 button is released
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - UP ==//
if (ctl->axisY() <= -100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisY(), -100, -508, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed up
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - DOWN ==//
if (ctl->axisY() >= 100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisY(), 100, 512, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, HIGH);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed down
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - LEFT ==//
if (ctl->axisX() <= -100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisX(), -100, -508, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, 0);
analogWrite(ENBpin, motorSpeed);
// code for when left joystick is pushed left
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK - RIGHT ==//
if (ctl->axisX() >= 100) {
int motorSpeed = map(ctl->axisX(), 100, 512, 70, 255);
digitalWrite(IN1pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4pin, LOW);
analogWrite(ENApin, motorSpeed);
analogWrite(ENBpin, 0);
// code for when left joystick is pushed right
}
//== LEFT JOYSTICK DEADZONE ==//
if (ctl->axisY() > -100 && ctl->axisY() < 100 && ctl->axisX() > -100 && ctl->axisX() < 100) {
analogWrite(ENApin, 0);
analogWrite(ENBpin, 0);
// code for when left joystick is at idle
}
//== RIGHT JOYSTICK - X AXIS ==//
if (ctl->axisRX()) {
// code for when right joystick moves along x-axis
}
//== RIGHT JOYSTICK - Y AXIS ==//
if (ctl->axisRY()) {
// code for when right joystick moves along y-axis
}
dumpGamepad(ctl);
}void processControllers() {
for (auto myController : myControllers) {
if (myController && myController->isConnected() && myController->hasData()) {
if (myController->isGamepad()) {
processGamepad(myController);
} else {
Serial.println("Unsupported controller");
}
}
}
}
// Arduino setup function. Runs in CPU 1
void setup() {
pinMode(ENApin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENBpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4pin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.printf("Firmware: %s\n", BP32.firmwareVersion());
const uint8_t* addr = BP32.localBdAddress();
Serial.printf("BD Addr: %2X:%2X:%2X:%2X:%2X:%2X\n", addr[0], addr[1], addr[2], addr[3], addr[4], addr[5]);
// Setup the Bluepad32 callbacks
BP32.setup(&onConnectedController, &onDisconnectedController);
// "forgetBluetoothKeys()" should be called when the user performs
// a "device factory reset", or similar.
// Calling "forgetBluetoothKeys" in setup() just as an example.
// Forgetting Bluetooth keys prevents "paired" gamepads to reconnect.
// But it might also fix some connection / re-connection issues.
BP32.forgetBluetoothKeys();
// Enables mouse / touchpad support for gamepads that support them.
// When enabled, controllers like DualSense and DualShock4 generate two connected devices:
// - First one: the gamepad
// - Second one, which is a "virtual device", is a mouse.
// By default, it is disabled.
BP32.enableVirtualDevice(false);
// Serial port for debugging purposes
}
// Arduino loop function. Runs in CPU 1.
void loop() {
// This call fetches all the controllers' data.
// Call this function in your main loop.
//Serial.println(readDHTTemperature());
//Serial.println(readDHTHumidity());
bool dataUpdated = BP32.update();
if (dataUpdated)
processControllers();
// The main loop must have some kind of "yield to lower priority task" event.
// Otherwise, the watchdog will get triggered.
// If your main loop doesn't have one, just add a simple `vTaskDelay(1)`.
// Detailed info here:
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/66278271/task-watchdog-got-triggered-the-tasks-did-not-reset-the-watchdog-in-time
// vTaskDelay(1);
delay(150);
}Aufgaben
- Die Aufgabenstellung für das Projekt findest du auf diesem Arbeitsblatt.
- Die Aufgabenstellung für das Projekt findest du auf diesem Arbeitsblatt.